So how old are you really?
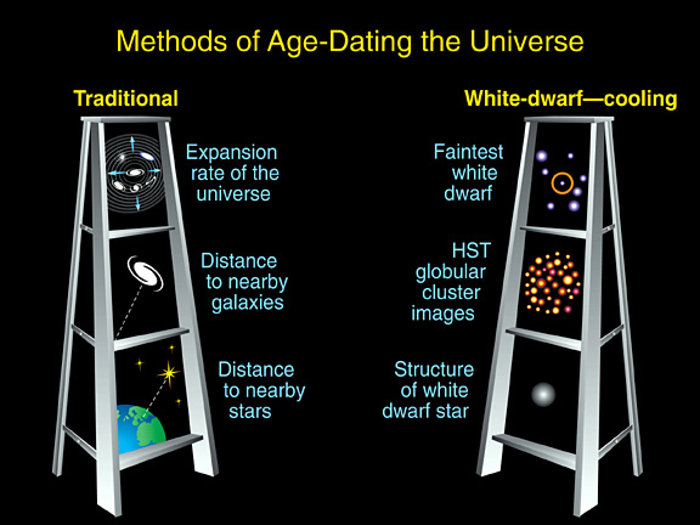
This illustration outlines the two techniques astronomers have used to determine the universe's age.
In the 'traditional method, ' astronomers used measurements of the universe's expansion rate to calculate the age of the cosmos. They determined the expansion rate by measuring the distances to nearby galaxies. They then compared those measurements with the speed at which those galaxies are receding from Earth. Astronomers used that data to calculate the universe's age.
In the 'white-dwarf-cooling method, ' astronomers studied the faintest white dwarfs in a globular cluster. Globular clusters are among the oldest clusters of stars in the universe. And the faintest and coolest white dwarfs within globular clusters represent the oldest stars in the clusters. Earlier Hubble observations showed that the first stars formed less than 1 billion years after the universe's birth in the big bang. So, finding the oldest stars puts astronomers within arm's reach of the universe's age.
Credit:About the Image
About the Object
| Name: | Age-Dating, Universe |
|---|---|
| Type: | Unspecified |
| Category: | Cosmology Illustrations |